What Is Carbolic Acid Used For
What is Carbolic Acid?
Carbolic acrid (ordinarily known as phenol) is an effluvious chemical molecule with the molecular formula C6H5OH and the molecular formula C6H5OH. It is a combustible white crystalline substance. Carbolic acid, simplest member of the phenol family unit of organic compounds.
Phenols are sometimes known equally carbolic acids considering of their extreme acerbity. Because of resonance, the phenol molecule has a partial positive charge on the oxygen atom, and the anion created past the loss of a hydrogen ion is similarly resonance stabilised. Phenol is hydroxybenzene by definition. The substance is known past the proper noun phenol. The IUPAC name for it would exist benzenol, which was derived similarly to the IUPAC names for aliphatic alcohols.
Table of Contents
- Carbolic Acid Formula
- Carbolic Acid Construction
- Carbolic Acid Properties
- Carbolic Acid Uses
- Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
Carbolic Acid Formula
The formula for carbolic acrid is Chalf-dozenH5OH.
Carbolic acid, likewise known as carbolic acid and phenolic acid, is a colourless, white crystalline solid at ambient temperature that is found naturally.
Carboxylic acids with a low molecular weight are usually liquids or solids with a low melting point. Well-nigh low molecular weight phenols are h2o soluble due to hydrogen bonding. Considering of stronger intermolecular hydrogen bonding, phenols have higher boiling temperatures than alcohols of the same molecular weight.
Carbolic Acid Construction
Phenol besides known as carbolic acid is an aromatic organic compound with the molecular formula C6H5OH. It is a white crystalline solid that is volatile.
The construction of Carbolic acrid (phenol) is given beneath.
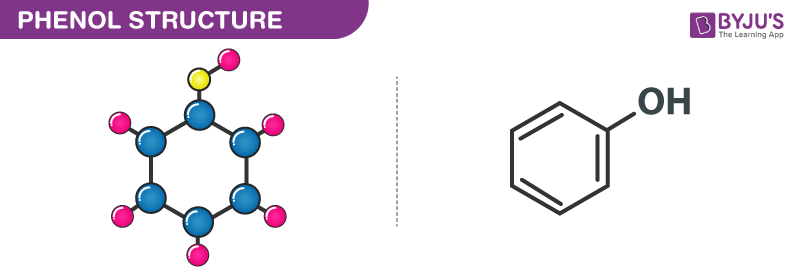
Carbolic Acid Properties
Concrete Properties of Carbolic Acrid
- Carbolic acid is a natural product.
- Carbolic acid is water soluble.
- Carbolic acrid is a mildly acidic substance.
- The carbolic acid is transformed to the phenolate ion in an aqueous medium.
- Carbolic acrid has resonance properties.
- Hydrogen bonds are formed by carbolic acid.
- Tautomerism is a belongings of carbolic acid.
Chemic Properties of Carbolic Acid
1. Addition of base of operations to the phenol
Phenol reacts with: A base of operations (similar NaOH) to form the phenoxide anion. This is a deprotonation reaction, due to the removal of the proton (hydrogen).
C6H5OH + NaOH → C6H5ONa + H2O
2. Addition of Acyl Group
A typical acyl chloride is ethanoyl chloride, CHthreeCOCl. Phenol reacts with ethanoyl chloride at room temperature, although the reaction isn't every bit fast equally the 1 between ethanoyl chloride and an alcohol. Phenyl ethanoate is formed together with hydrogen chloride gas.
C6H5OH + C6H5COCl → C6H5OCOC6H5 + HCl
3. Reduction under zinc grit
Distillation of phenol with zinc-dust gives benzene and ZnO as a side-product.
C6H5OH + Zn → C6H6 + ZnO
4. Oxidation of phenol
Oxidation of phenols gives benzoquinone. Phenols are more than readily oxidised than alcohols. Oxidation tin exist done past using strong oxidising agents like chromic acid, silvery oxide, etc. When phenol is oxidised using chromic acid in presence of sulphuric acid and h2o it forms benzoquinone.
Carbolic Acid Uses
The use of carbolic acid on metal surfaces at loftier temperatures increases the gamble of corrosion on steel. The corrosion charge per unit of low-carbon steel has been observed to be reduced when metal surfaces are exposed to carbolic acrid and moisture in the 0.2 per centum to 0.6 per centum range.
All the same, when the moisture level rose, so did the rate of deterioration. Corrosion of depression-carbon steel is substantially accelerated at temperatures exceeding 200°C. Furthermore, carbolic acrid containing substantial sulphur is more corrosive to certain metals than pure carbolic acrid.
Plastics precursors are the most prevalent usage of phenol, accounting for 2-thirds of its full use. Bisphenol-A, a major precursor to polycarbonates and epoxide resins, is produced by condensation of bisphenol-A with acetone. phenolic resins, such as bakelite, are generated when phenol, alkylphenols, or diphenols react with formaldehyde to form phenolic resins. When phenol is partially hydrogenated, cyclohexanone is generated, which is a precursor to nylon. Nonylphenol is produced via alkylation of phenol, which is subsequently ethoxylated to produce nonionic detergents.
Frequently Asked Questions on Carbolic Acid
What is carbolic acid used for?
Phenol (carbolic acid) is one of the oldest clarified agents. Apart from being used in many commercially bachelor products, in rural Republic of india, it is frequently used in the household to prevent snake infestation.
Is phenol and carbolic acrid the aforementioned?
Phenol, a colourless, white crystalline solid at room temperature, likewise known as carbolic acid and phenolic acid, is an organic compound that is institute naturally.
What is hydroxy benzene used for?
A caustic, poisonous, white crystalline chemical compound, C6H5OH, derived from benzene and used in resins, plastics, and pharmaceuticals and in dilute form equally a disinfectant and clarified.
What is resorcinol made of?
Resorcinol, as well called m-dihydroxybenzene, is a phenolic compound used in the manufacture of resins, plastics, dyes, medicine, and numerous other organic chemic compounds. It is produced in large quantities by sulfonating benzene with fuming sulfuric acid and fusing the resulting benzenedisulfonic acid with caustic soda.
What is naphthol used for?
The chemical compound ane-naphthol, or α-naphthol, fabricated by heating 1-naphthalenesulfonic acid with caustic alkali or past heating 1-naphthylamine with h2o nether pressure, is used directly in making several dyes, and large amounts of it are converted to compounds ultimately incorporated into other dyes.
What Is Carbolic Acid Used For,
Source: https://byjus.com/chemistry/carbolic-acid/
Posted by: motenbobyth.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Is Carbolic Acid Used For"
Post a Comment